What is Mutual Funds?
We believe that money is very important part in our life. This data is gathered with only intention of creating awareness and we do not have purpose of selling a scheme, a product or offering any type of investment advice. kindly consider all the material of this page as educational purpose only. Information published in this page has been obtained from source considered to be authentic. Nothing contained here should be construed as investment advice or recommendation to buy/sell/hold any investment product.
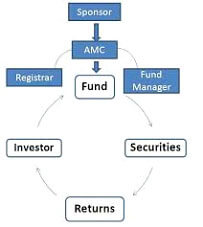
A mutual fund is just the connecting bridge or a financial intermediary that allows a group of investors to pool their money together with a predetermined investment objective.
Professional Management: The mutual fund will have a fund manager who is responsible for investing the gathered money into specific securities (stocks or bonds).
Fund ownership: When you invest in a mutual fund, you are buying units or portions of the mutual fund and thus on investing becomes a shareholder or unit holder of the fund.
Mutual Funds are Diversified
Mutual funds are considered as one of the best available investments as compared to others. They are very cost efficient and also easy to invest in, thus by pooling money together in a mutual fund, investors can purchase stocks or bonds with much lower trading costs than if they try to do it on their own. But the biggest advantage to mutual funds is diversification, by minimizing risk & optimizing returns.
How are mutual funds regulated?
SEBI and/or the RBI (in case the AMC is promoted by a bank) regulates all Asset Management Companies (AMCs).In addition, every mutual fund has a Trustee who represents the unit holders' interests in the mutual fund.
Mutual fund Objective
For example, an objective of a growth stock fund might be: This fund invests primarily in the equity markets with the objective of providing long-term capital appreciation towards meeting your long-term financial needs such as retirement or a child’s education.
Depending on investment objectives, funds can be broadly classified in the following types:
1. Equity fund:
These funds invest a maximum part of their corpus into equities holdings. The structure of the fund may vary for different schemes and the fund manager’s outlook on different stocks. The Equity Funds are sub-classified depending upon their investment objective, as follows:
- Large Cap Fund
- Diversified Equity Funds
- Mid-Cap Funds
- Small Cap Funds
- Sector Specific Funds
- Tax Savings Funds (ELSS)
Equity investments are meant for a longer time horizon, thus Equity funds rank high on the risk-return matrix.
2. Debt Funds:
The objective of these Funds is to invest in debt papers. Government authorities, private companies, banks and financial institutions who are some of the major issuers of debt papers. By investing in debt instruments, these funds ensure low risk and provide stable income to the investors. Debt funds are further classified as:
Gilt Funds: Invest their corpus in securities issued by Government, popularly known as Government of India debt papers. These Funds carry zero Default risk but are associated with Interest Rate risk. These schemes are safer as they invest in papers backed by Government.
Income Funds: Invest a major portion into various debt instruments such as bonds, corporate debentures and Government securities.
MIPs: Invests maximum of their total corpus in debt instruments while they take minimum exposure in equities. It gets benefit of both equity and debt market. These scheme ranks slightly high on the risk-return matrix when compared with other debt schemes.
Short Term Plans (STPs): Meant for investment horizon for three to six months. These funds primarily invest in short term papers like Certificate of Deposits (CDs) and Commercial Papers (CPs).
Liquid Funds: Also known as Money Market Schemes, these funds provides easy liquidity and preservation of capital. These schemes invest in short-term instruments like Treasury Bills, inter-bank call money market, CPs and CDs. These funds are meant for short-term cash management of corporate houses and are meant for an investment horizon of 1day to 3 months. These schemes rank low on risk-return matrix and are considered to be the safest amongst all categories of mutual funds.
3. Hybrid funds:
As the name suggest they, are a mix of both equity and debt funds. They invest in both equities and fixed income securities, which are in line with pre-defined investment objective of the scheme. These schemes aim to provide investors with the best of both the worlds. Equity part provides growth and the debt part provides stability in returns.
Advantages
of Mutual Funds
Professional Management
The basic advantage of funds is that, they are professional managed, by well qualified professionally. Investors purchase funds because they do not have the time or the expertise to manage their own portfolio. A mutual fund is considered to be relatively less expensive way to make and monitor their investments.
Diversification
Purchasing units in a mutual fund instead of buying individual stocks or bonds, the investors risk is spread out and minimized up to certain extent. The idea behind diversification is to invest in a large number of assets so that a loss in any particular investment is minimized by gains in others.
SIMPLICITY
Investments in mutual fund is considered to be easy, compare to other available instruments in the market, and the minimum investment is small. Most AMC also have automatic purchase plans whereby as little as Rs. 2000, where SIP start with just Rs.500 per month basis.
ECONOMIES OF SCALE
Mutual fund buy and sell large amounts of securities at a time, thus help to reducing transaction costs, and help to bring down the average cost of the unit for their investors.
LIQUIDITY
Just like an individual stock, mutual fund also allows investors to liquidate their holdings as and when they want.
NON GUARANTEED PRODUCT
Mutual fund is pool of investors' money managed by fund managers. Fund Managers primarily invest in stock market and money market. While stock market carries volatility risk, money market involves credit/default risk and interest rate risk. Hence making mutual funds a Non Guaranteed investment product.
